
In a Covered Aerial MV (Spacer Cable), spacers hold three MV phase conductors in close approximation.Spacers are suspended from a high-strength messenger wire. Covered Aerial cable itself is a single aluminum conductor protected by a layer of track-resistant polyethylene.
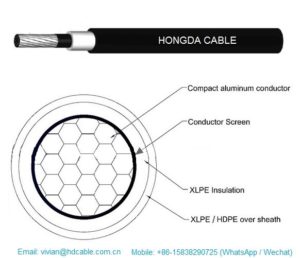
Application: Overhead single core cables with aluminum conductor and three layer of insulation, for overhead power transmission and distribution lines up to 33 Kv.
ENGINEERING SPECIFICATIONS
STANDARD according to Hendrix specification.
Rated Voltage 12/20kv or 18/30 kv.
Conductor stranded with compress concentric 1350-H19 wires .
Core the conductor is insulated with a three layer of extruded compound.
Operating temperature 90°c continues normal operation.
Features and Benefits The covering provides mechanical protection to the Conductor and it is resistant to weathering and chemicals. If the conductors accidentally come into contact due to high winds, falling tree limbs or other disturbances, the covering resists short circuits and the tendency for conductors to weld together.
Spacer cables characteristics and advantage Spacer cables provide a simple, reliable and cost-effective alternative And also add value to the network, requiring very little maintenance during its entire Lifespan .
Under grounding conductors in these areas can be impractical and have significant economic implications.
Spacer cables are installed in areas where the need for an insulated overhead distribution network is desirable. These areas include, but not limited to Hilly and mountainous areas.
Network reliability is vulnerable in these areas because of conductor clashing caused during high winds and storms and falling trees and branches
These areas are also more prone to lightning strikes
River Crossings.
Bushfire Danger Areas In the unlikely event that conductors clash, for whatever reason .
Advantages of spacer cables and comparing with medium voltage Aerial Bundled cables:
1 – Troubleshooting Aerial Bundled cables is difficult due to complexity and so is to repair whereas in spacer-cable network this issue has been addressed and solved
2 – The cost of constructing an aerial spacer cable network equals %60 of the network with Aerial Bundled cables
3 – Spacer cable distribution networks are simple and do not require special fittings, equipment or instructions in comparison with Aerial Bundled cables networks
4 – Acquiring splitting and attaching a transformer in medium voltage Aerial Bundled cables networks is extremely difficult whereas in spacer cable networks this issue has been alleviated and improved
5 – Spacer cables are lighter than Aerial Bundled cables and so they require less pole stability power
The advantages of spacer cables with Medium voltage overhead covered conductors:
1 – All aluminum conductors can be utilized
2 – Extra lightning protection equipment are not needed
3 – Insulators are not needed
4 – Adjacency band limitations are decreased
5 – Multiple feeders can be fitted on one pole
6 – Can be passed through large spans
Space Aerial Cable STRUCTURE:
| NUMBER OF CORE | Single core |
| 1. CONDUCTOR |
|
| 2. CONDUCTOR SHIELD | Semi conducting cross-linked polyethylene |
| 3. INSULATION |
|
| 4. SHEATH |
|
| CLASSIFICATION |
|
Space Aerial Cable Specifications:
| Nominal Sectional Area | Minimum Number of wire | Diameter of Conductor (approx.) | Thickness of Insulation | Thickness of sheath | Overall Diameter (approx.) | Maximum DC. conductor resistance at 20°C | Allowable ampacities in free air at 40°C ambient | Cable weight (approx.) | Standard packing |
| mm2 | NO | mm | mm | mm | mm | Ω / km | A | kg/km | m |
| 25 | 7 | 5.9 | 4.45 | 3.18 | 20.0 | 1.200 | 119 | 380 | 1000/D |
| 35 | 7 | 6.95 | 4.45 | 3.18 | 21.0 | 0.868 | 149 | 490 | 1000/D |
| 50 | 7 | 8.33 | 4.45 | 3.18 | 22.0 | 0.641 | 186 | 530 | 1000/D |
| 70 | 18 | 9.73 | 4.45 | 3.18 | 24.5 | 0.443 | 229 | 630 | 1000/D |
| 95 | 18 | 11.45 | 4.45 | 3.18 | 26.0 | 0.320 | 279 | 750 | 1000/D |
| 120 | 18 | 12.95 | 4.45 | 3.18 | 27.0 | 0.253 | 321 | 850 | 1000/D |
| 150 | 18 | 14.27 | 4.45 | 3.18 | 29.5 | 0.206 | 371 | 960 | 1000/D |
| 185 | 34 | 15.98 | 4.45 | 3.18 | 31.0 | 0.164 | 429 | 1100 | 1000/D |
| 240 | 34 | 18.47 | 4.45 | 3.18 | 33.5 | 0.125 | 520 | 1400 | 1000/D |
Technical Specification According To Hendrix
| Aerial Spacer Cable 20 kv | ||||||||||
| Crossectional | Conductor Construction | Conductor Dia. | Thickness | Approx. Overal dia | Electical Rwesistance | Calc. Breaking Force | Air Flow Capacity at 200 c | Approx. Conductor Weight | ||
| Semi Conductor | Insulation | Jacket | ||||||||
| Mm2 | Nxmm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | Ω/km | N | A | Kg/km |
| 70 | 12×2.77 | 10 | 0.4 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 23.5 | 0.443 | 10.420 | 229 | 509 |
| 120 | 15×3.30 | 13.2 | 0.4 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 26.7 | 0.253 | 18.518 | 321 | 729 |
| 150 | 15×3.66 | 14.8 | 0.4 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 28.4 | 0.206 | 22.457 | 371 | 826 |
| 185 | 30×2.88 | 16.2 | 0.4 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 29.7 | 0.164 | 28.974 | 429 | 959 |
| Aerial Spacer Cable 33 kv | ||||||||||
| 70 | 12×2.77 | 10 | 0.4 | 4.5 | 3.2 | 26.0 | 0.443 | 10.420 | 227 | 630 |
| 120 | 15×3.30 | 13.2 | 0.4 | 4.5 | 3.2 | 29.3 | 0.253 | 18.518 | 318 | 850 |
| 150 | 15×3.66 | 14.8 | 0.4 | 4.5 | 3.2 | 30.8 | 0.206 | 22.457 | 367 | 960 |
| 185 | 30×2.88 | 16.2 | 0.4 | 4.5 | 3.2 | 32.2 | 0.164 | 28.974 | 425 | 1100 |